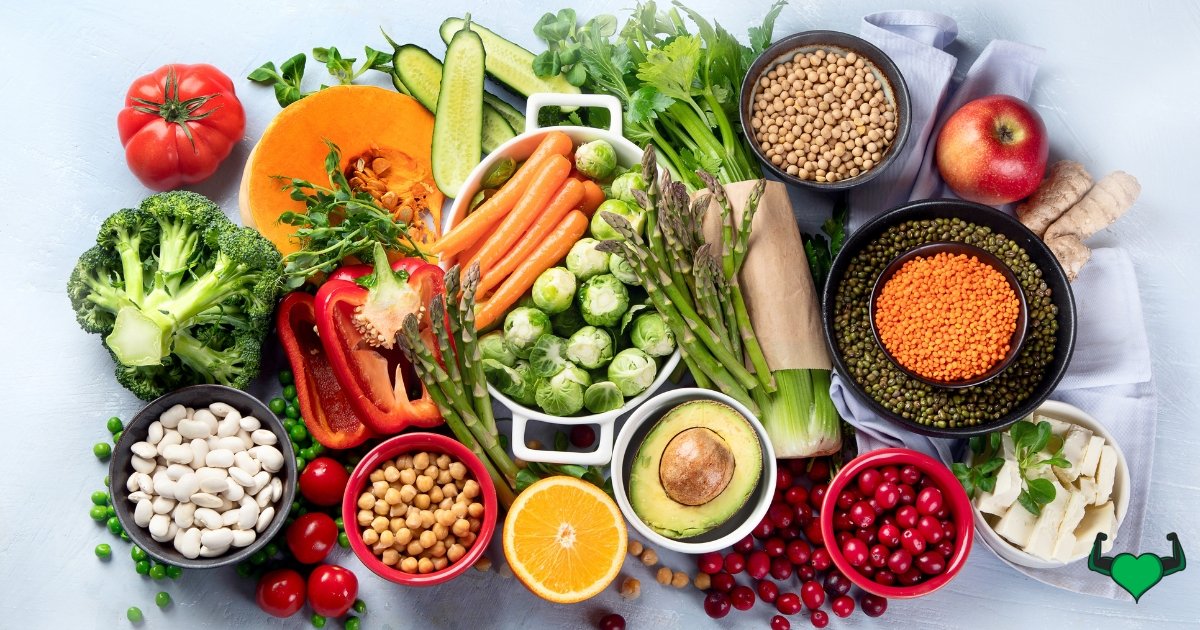
Transitioning to or maintaining a vegan diet is a powerful way to align your lifestyle with ethical, environmental, and health values. But there’s more to it than just cutting out animal products—balancing your macronutrients is key to ensuring you stay energized and nutritionally satisfied. Whether you’re a seasoned vegan or just starting out, mastering the balance of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates is crucial for thriving on this plant-based journey. Let’s dive into the essentials of balancing macronutrients on a vegan diet, ensuring you’re getting everything your body needs!
This website may contain affiliate links. If you make a purchase through these links, I may earn a commission at no extra cost to you. Thank you for supporting this site.
Table of Contents
Understanding Macronutrients on a Vegan Diet

Definition and importance of macronutrients: protein, fats, and carbohydrates
Macronutrients—protein, fats, and carbohydrates—are the three main nutrients your body needs for energy, growth, and overall health. Protein is essential for muscle repair and immune function, fats support hormone production and brain health, and carbohydrates are the primary source of energy. When balancing macronutrients on a vegan diet, it’s important to choose plant-based sources such as legumes for protein, nuts and seeds for healthy fats, and whole grains for carbohydrates. Achieving the right balance ensures you get the nutrients necessary to thrive on a vegan diet, supporting everything from energy levels to nutrient absorption.
How macronutrient needs differ in a vegan diet compared to omnivorous diets
In a vegan diet, macronutrient needs differ from omnivorous diets primarily in protein and fat sources. Vegans must rely on plant-based proteins, like legumes and tofu, which may require combining foods to get all essential amino acids. Fats are sourced from nuts, seeds, and avocados instead of animal products, with a focus on balancing omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. Carbohydrates in vegan diets often come from whole grains and vegetables. Balancing macronutrients on vegan diet requires careful planning to ensure adequate intake of all essential nutrients, particularly protein and healthy fats, to match the diverse sources available in omnivorous diets.
Common misconceptions about macronutrient intake in veganism
A common misconception about macronutrient intake in veganism is that it’s difficult to get enough protein. In reality, a well-planned vegan diet can provide ample protein from sources like legumes, tofu, and quinoa. Another myth is that vegan diets are low in healthy fats, but foods like avocados, nuts, and seeds offer abundant fats, including essential omega-3s. Finally, some believe that vegans only consume carbohydrates, but balancing macronutrients on vegan diet involves carefully choosing a mix of proteins, fats, and complex carbs to meet all nutritional needs effectively.
Protein Sources for Vegans

Importance of protein in the body: muscle repair, immune function, and more
Protein is vital for the body, playing a key role in muscle repair, immune function, and overall cell health. It provides the building blocks (amino acids) needed for tissue growth and recovery, especially after exercise. Protein also supports the production of antibodies, crucial for a strong immune system. When [balancing macronutrients on a vegan diet], it’s essential to include protein-rich plant foods like legumes, tofu, and quinoa to ensure your body gets the necessary nutrients for these critical functions.
High-protein plant foods: legumes, tofu, tempeh, seitan, quinoa, and more
When balancing macronutrients on vegan diet, high-protein plant foods are essential. Legumes like lentils, chickpeas, and black beans are excellent protein sources, rich in fiber and nutrients. Tofu and tempeh, made from soybeans, offer versatile, protein-packed options. Seitan, derived from wheat gluten, is another high-protein choice with a meat-like texture. Quinoa, a complete protein, provides all essential amino acids. Including these foods in your diet ensures you meet your protein needs while maintaining a balanced vegan diet.
Complete proteins and combining foods for a full amino acid profile
Complete proteins contain all nine essential amino acids needed for the body, which are crucial for functions like muscle repair and immune support. While most plant foods are not complete proteins, you can achieve a full amino acid profile by combining different foods. For example, pairing rice with beans or whole grains with legumes creates a complete protein. Balancing macronutrients on vegan diet involves strategically combining these foods to ensure you get all essential amino acids, supporting overall health and vitality.
Tips for ensuring adequate protein intake on a daily basis
To ensure adequate protein intake while balancing macronutrients on vegan diet, start by incorporating high-protein foods like legumes, tofu, tempeh, and quinoa into every meal. Diversify your protein sources to include nuts, seeds, and whole grains. Consider using plant-based protein powders if you have higher protein needs, such as for muscle building. Spread your protein intake throughout the day to optimize absorption and muscle repair. By planning meals around these protein-rich foods, you can easily meet your daily protein requirements.
Healthy Fats in a Vegan Diet
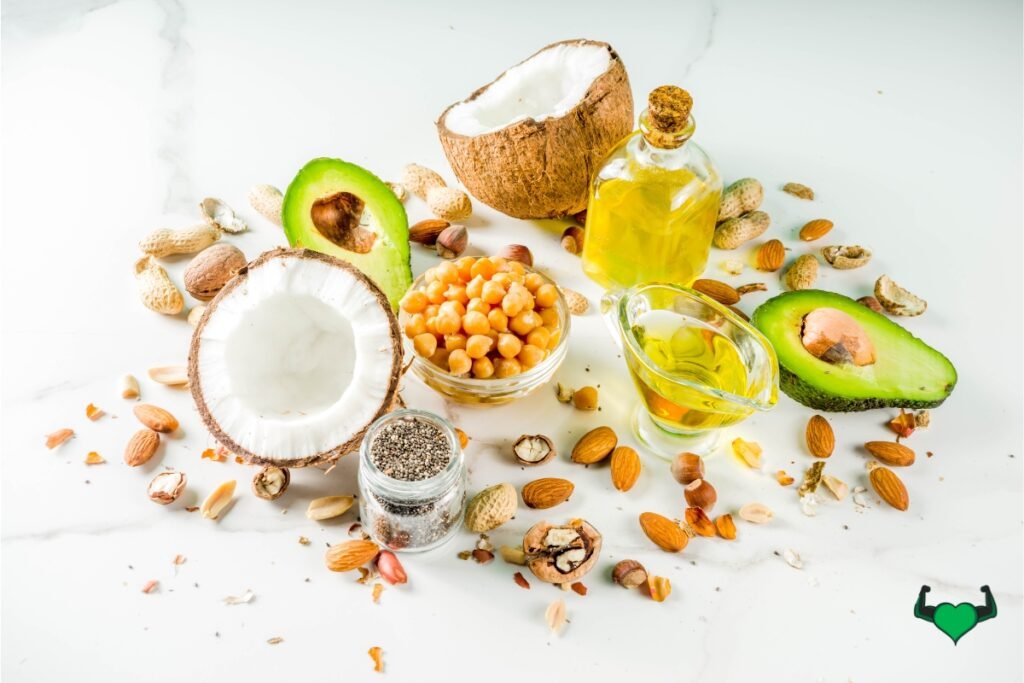

Role of fats in hormone production, brain health, and absorption of vitamins
Fats play a crucial role in hormone production, brain health, and the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K). Healthy fats from sources like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil support the production of hormones, essential for regulating bodily functions. They also contribute to brain health by providing structural components for brain cells. Additionally, fats enhance the absorption of key vitamins, ensuring your body gets the nutrients it needs. When balancing macronutrients on vegan diet, including a variety of healthy fats is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being.
Best sources of healthy fats: avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil
It’s important to include healthy fats for optimal health when balancing macronutrients on vegan diet. Avocados are rich in monounsaturated fats that support heart health. Nuts, such as almonds and walnuts, provide a mix of healthy fats and essential omega-3 fatty acids. Seeds, like chia and flaxseeds, are excellent sources of omega-3s and fiber. Olive oil is another key source of monounsaturated fats, beneficial for brain and heart health. Incorporating these foods into your diet ensures you get the healthy fats necessary for hormone production, brain function, and nutrient absorption.
Balancing Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids: flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts
If you are a vegan it’s crucial to manage your intake of Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids. While Omega-6 fatty acids are abundant in many plant oils and processed foods, Omega-3s are less common. To balance these fatty acids, focus on incorporating Omega-3-rich foods like flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts into your diet. These foods help reduce inflammation and support heart and brain health, ensuring a healthier ratio between Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids on a vegan diet.
Avoiding unhealthy fats: processed oils and trans fats
When balancing macronutrients on vegan diet, it’s important to avoid unhealthy fats like processed oils and trans fats, which are often found in fried foods and packaged snacks. These fats can lead to inflammation, heart disease, and other health issues. Instead, focus on consuming whole, unprocessed sources of healthy fats, such as avocados, nuts, and seeds. Prioritizing natural fats over processed ones supports better overall health and helps maintain a balanced macronutrient profile on a vegan diet.
Carbohydrate Choices for Sustained Energy

Carbohydrates as the body’s primary energy source
Carbohydrates are the body’s primary energy source, fueling everything from daily activities to intense workouts. When balancing macronutrients on vegan diet, it’s essential to choose complex carbohydrates like whole grains, starchy vegetables, and fruits. These provide sustained energy and support stable blood sugar levels. Unlike simple carbs, complex carbs also offer fiber, which aids digestion and keeps you full longer. Prioritizing the right types of carbs ensures consistent energy levels throughout the day while maintaining a balanced diet.
Differentiating between simple and complex carbohydrates
When balancing macronutrients on vegan diet, it’s important to differentiate between simple and complex carbohydrates. Simple carbohydrates, found in foods like sugar, white bread, and pastries, are quickly digested, leading to rapid spikes and crashes in blood sugar levels. In contrast, complex carbohydrates, found in whole grains, legumes, and vegetables, digest more slowly, providing steady energy and lasting fullness. Focusing on complex carbs supports better blood sugar control, sustained energy, and overall health. Prioritizing these in your diet helps maintain a balanced macronutrient intake.
Best sources of complex carbs: whole grains, starchy vegetables, and fruits
The best sources of complex carbs for vegans include whole grains, starchy vegetables, and fruits. Whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, and oats provide sustained energy and are rich in fiber. Starchy vegetables such as sweet potatoes, squash, and corn offer a nutrient-dense source of carbohydrates. Fruits like apples, berries, and bananas also provide complex carbs along with vitamins and antioxidants. Incorporating these foods ensures steady energy levels and supports overall health on a vegan diet.
Importance of fiber: promoting digestive health and stable blood sugar levels
Fiber is crucial for promoting digestive health and maintaining stable blood sugar levels. It helps regulate bowel movements, preventing constipation, and supports a healthy gut microbiome. Additionally, fiber slows the absorption of sugar, which prevents blood sugar spikes and crashes, keeping energy levels stable. When balancing macronutrients on vegan diet, incorporating fiber-rich foods like whole grains, legumes, fruits, and vegetables is essential for optimal digestive health and consistent blood sugar control.
Balancing Macronutrients in Vegan Meal Planning
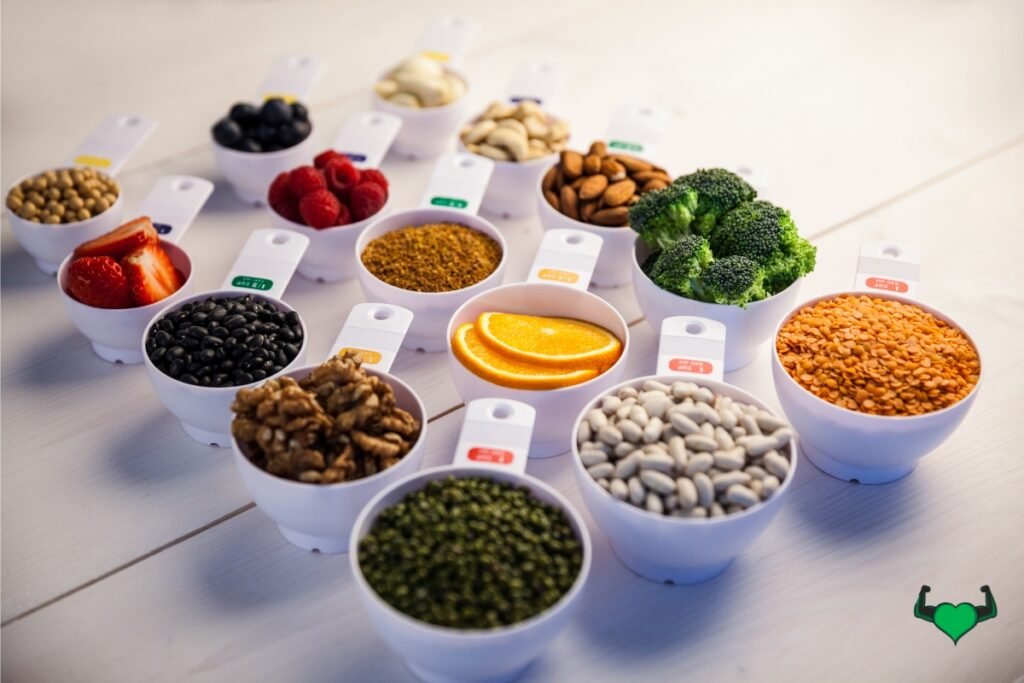

Strategies for creating balanced vegan meals: the plate method, portion control
When balancing macronutrients on vegan diet, using the plate method and practicing portion control are effective strategies. The plate method involves dividing your plate into sections: half for vegetables and fruits, a quarter for whole grains, and a quarter for protein sources like legumes or tofu. This ensures a balanced intake of carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats. Portion control helps manage calorie intake while maintaining the right balance of nutrients, preventing overeating and supporting overall health. By following these strategies, you can create well-rounded, nutrient-dense vegan meals.
Meal prepping tips to ensure a balanced intake throughout the week
To ensure a balanced intake throughout the week while balancing macronutrients on vegan diet, meal prepping is key. Start by planning meals that include a mix of proteins, healthy fats, and complex carbs, like quinoa, tofu, and leafy greens. Batch-cook grains, legumes, and roasted vegetables to have ready-to-eat options on hand. Store meals in portioned containers to control serving sizes and maintain nutrient balance. Including a variety of foods in your prep helps avoid monotony and ensures you meet your nutritional needs all week long.
Sample meal plans and recipes that balance macronutrients effectively
For balancing macronutrients on vegan diet, here are sample meal plans that effectively balance proteins, fats, and carbohydrates:
Breakfast:
- Overnight oats with chia seeds, almond butter, and mixed berries.
- Balances: Complex carbs from oats, healthy fats from chia seeds, and protein from almond butter.
Lunch:
- Quinoa salad with chickpeas, avocado, kale, and a tahini dressing.
- Balances: Protein from chickpeas, healthy fats from avocado, and complex carbs from quinoa.
Dinner:
- Stir-fried tofu with brown rice, broccoli, and sesame seeds.
- Balances: Protein from tofu, complex carbs from brown rice, and healthy fats from sesame seeds.
These meals provide a well-rounded approach to maintaining a balanced vegan diet, ensuring you get all necessary macronutrients throughout the day.
Adjusting macronutrient ratios based on individual goals: weight loss, muscle gain, or maintenance
When balancing macronutrients on vegan diet, adjusting macronutrient ratios based on your goals is key. For weight loss, increase protein and fiber intake to promote satiety while reducing overall calories, focusing on foods like legumes and vegetables. For muscle gain, prioritize higher protein intake, incorporating more tofu, tempeh, and protein-rich grains like quinoa, while slightly increasing healthy fats for energy. For maintenance, aim for a balanced ratio with a moderate intake of proteins, fats, and complex carbs to sustain energy and health. Tailoring these ratios helps you achieve specific fitness and health goals effectively.
Overcoming Common Challenges in Macronutrient Balance

Managing macronutrient intake when dining out or on the go
For balancing macronutrients on vegan diet while dining out or on the go, choose meals that include a good mix of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. Opt for dishes with beans, tofu, or quinoa for protein, paired with whole grains and vegetables. Avoid deep-fried or heavily processed foods, which can add unhealthy fats. If options are limited, carry healthy snacks like nuts, seeds, or fruit to help fill nutritional gaps. Request dressings and sauces on the side to control fat intake, and don’t hesitate to customize orders to meet your macronutrient needs.
Addressing potential nutrient deficiencies: B12, iron, and calcium
It’s crucial to address potential nutrient deficiencies in B12, iron, and calcium when balancing macronutrients on vegan diet. Vitamin B12 is not naturally found in plant foods, so include fortified foods or take a B12 supplement. For iron, focus on consuming lentils, beans, and leafy greens, and pair them with vitamin C-rich foods to enhance absorption. Calcium can be obtained from fortified plant milks, tofu, and leafy greens like kale. Regularly including these nutrients in your diet ensures you meet your nutritional needs and avoid deficiencies.
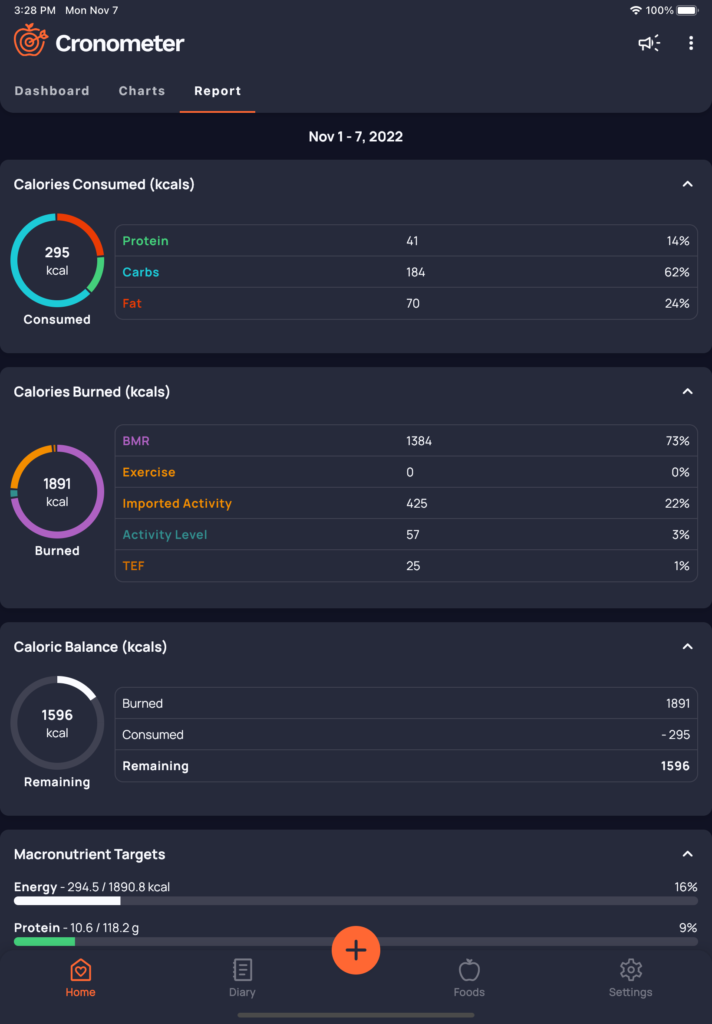
Tools and apps for tracking macronutrient intake on a vegan diet
To assist with balancing macronutrients on vegan diet, various tools and apps can help you track your intake effectively. Apps like Cronometer and MyFitnessPal allow you to log meals and track macronutrients, including protein, fats, and carbohydrates. These apps also offer nutrient breakdowns to monitor vitamins and minerals like B12, iron, and calcium. Additionally, they provide personalized insights, making it easier to adjust your diet according to your health goals, whether it’s weight loss, muscle gain, or maintenance. Using these tools helps ensure you stay on track with your vegan diet’s macronutrient needs.
Conclusion
Balancing macronutrients on a vegan diet doesn’t have to be complicated! By understanding the role of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates in your diet, and knowing where to source them, you can create meals that nourish your body and keep you feeling your best. Whether your goal is to improve your overall health, achieve specific fitness milestones, or simply maintain your energy levels, this guide offers the tools and tips you need to succeed. Ready to take control of your nutrition? Start planning your balanced vegan meals today!